 There’s so much adventure and wonderment for young eyes, and it can take place with these wonderful items: Butterfly Tattoos, Backpack Explorer Kits (On the Nature Trail, Bug Hunt, Discovering Plants and Flowers) and Nature Smarts Workbooks for various ages.
There’s so much adventure and wonderment for young eyes, and it can take place with these wonderful items: Butterfly Tattoos, Backpack Explorer Kits (On the Nature Trail, Bug Hunt, Discovering Plants and Flowers) and Nature Smarts Workbooks for various ages.
Blog
Super Illuminated Loupe
 This very small, extremely high quality 12x power magnifier is great for getting a closer look at what’s bugging your plants, taking out splinters, or helping to identify flowers.
This very small, extremely high quality 12x power magnifier is great for getting a closer look at what’s bugging your plants, taking out splinters, or helping to identify flowers.
We also offer other affordable, high-quality magnification tools, such as Binoculars!
Stella Natura Astrological Planting Calendar 2026
 The Stella Natura Wall Calendar is an easy-to-use, informative and beautiful planting and gardening calendar that shows the best times to take advantage of the cosmic influences of the moon, sun and planets. This is a research-based system that is used by Biodynamic farmers and gardeners.
The Stella Natura Wall Calendar is an easy-to-use, informative and beautiful planting and gardening calendar that shows the best times to take advantage of the cosmic influences of the moon, sun and planets. This is a research-based system that is used by Biodynamic farmers and gardeners.
We have been using this calendar for over 25 years and believe it has helped with germination of seeds, root development of cuttings, and healthy plant development. More than just a calendar – it’s packed with valuable information and insights for successful growing, from seed to harvest!
Wildflowers of the Rocky Mountain Region
 Wildflowers of the Rocky Mountain Region, the most complete, up-to-date field guide for identifying a huge number of our wildflowers. All of the plants are described, located, and photographed, and arranged in an easy-to-use format.
Wildflowers of the Rocky Mountain Region, the most complete, up-to-date field guide for identifying a huge number of our wildflowers. All of the plants are described, located, and photographed, and arranged in an easy-to-use format.
ZomeTool
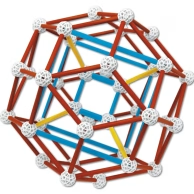
So what is the Zometool? Atomic Tinkertoy? Lego of the Future? Molecular modeling kit on steroids?
All of the above, and more! Quantum mathematician Micho Durdevich calls the Zometool a physical embodiment of quantum math: “It’s math you can feel.” If you think you’re “bad at math,” think again: this elegant tool makes it beautiful, simple and fun. The Zometool enhances creativity and intelligence. When you share the Zometool with children, you will be making an important investment in their future.
We couldn’t have a Science section for kids of all ages without the Zometool!
BUILDING TOPSOIL AND SOIL FERTILITY by Mikl Brawner
“Where can I get some good topsoil?” That’s a question I hear frequently at our nursery. And I often look wistfully towards the plains and say, only half-jokingly, “You can get good topsoil about 800 miles east of here.” That’s where I grew up, in Iowa, and where two tomato plants feed a family of six. It’s not that local suppliers are trying to deceive us when they sell Colorado clay as topsoil; it’s just that the glaciers didn’t dump three feet of loam on top of our clay.[Read More]
Robin Chocolate

We’re happy to once again bring you Robin’s wonderful, locally-crafted chocolate truffles! Robin Autorino is an award winning chocolatier and has been named by Dessert Professional as one of the Top Ten Chocolatiers in North America in 2013. We also offer her chocolate-drizzled crystallized ginger, chocolate-covered almonds and chocolate-covered pretzels!
Native Plants In Harlequin’s Gardens Display Gardens
Achillea lanulosa (Achillea millefolium var. lanulosa) (Yarrow)
Agave havardii (Havard’s Century Plant)
Agave parryi neomexicana (New Mexico Century Plant)
Amelanchier alnifolia (Serviceberry)
Amorpha canescens (Leadplant)
Amorpha fruticosa (False Indigo)[Read More]
St. Clair’s Organic Mints, Candies, Pastilles & Lozenges
 Yea – totally organic! Made by herbalist Debra St. Claire! No corn syrup! Delicious! Effective! Packaged in pretty, reusable tins (some staff use these for seed saving)! Incredibly inexpensive! Lots of flavors! Great stocking stuffers!
Yea – totally organic! Made by herbalist Debra St. Claire! No corn syrup! Delicious! Effective! Packaged in pretty, reusable tins (some staff use these for seed saving)! Incredibly inexpensive! Lots of flavors! Great stocking stuffers!
Merigold’s Skin Products
Merigold is a natural, organic skincare company based in Colorado and focused on holistic wellness. As a nurse, mother, natural food chef, and nutritionist, the owner has seen firsthand the toll constant striving takes on the body—it’s true, she says, the body does keep the score. She started Merigold to empower women to take a pause with nourishing, clean skincare products with clean skincare that was formulated to be effective, good for your body, and delightful to use.
We feature Merigold’s unique facial masks and bath soaks.
Plum Botanicals – Harlequin’s Exclusive!
The Spanish word ‘trementina’ has come to be used as the name for the sap of the pinyon tree of New Mexico. Folk remedies made from this sap have been used for centuries to relieve dry, cracked skin, abrasions and scrapes, and for drawing out splinters, and it really works! The pinyon sap and beeswax also contribute a wonderful aroma!
Made in New Mexico’s ‘curandera’ tradition by our friend Pamela, who climbed the pinyon trees to gather the sap, purified it, and infused it in olive oil and beeswax to create this rare traditional salve. Each tin of salve comes in a lovely organza gift bag.
Wander Hot Cocoa Mix

Kiersti and Pete love Colorado winters and enjoy long, cold days on the trails and slopes, followed by a real cup of rich, creamy hot cocoa. All the mixes they tried were watery, flavorless, and made with junk ingredients. So, they decided to make their own delicious mix, with just four ingredients: milk powder, cane sugar, premium cocoa powder, and a dash of salt. Just add hot water and stir! No need to bring milk with you on a camping trip, or have it in the fridge.
Wander Premium Cocoa Mix is made in Golden, and we carry their regular and single serving bags. Both are perfect stocking-stuffers for young and old!
Purple Fence Farm
Purple Fence Farm and Apothecary is located just north of Denver. What sets them apart in the world of skincare is their unwavering commitment to sustainability and simplicity. Every step, from hand planting our fields of lavender to handcrafting each balm and blend, is infused with passion and love.
With an emphasis on all-natural ingredients, and sustainable packaging, Purple Fence offers products that are not only effective and luxurious but also kind to our planet. We’re glad to bring their soaps to you!
Kisu Lip Balm – Harlequin’s Exclusive!
 Created by Pamela Clum’s Plum Botanicals, a small fair-trade organic skin-care line based here in Boulder Valley. This long-lasting lip balm is based on wild-collected African shea butter from a women’s cooperative, and lightly scented with the marvelous, unique, citrus-y essential oil of neroli.
Created by Pamela Clum’s Plum Botanicals, a small fair-trade organic skin-care line based here in Boulder Valley. This long-lasting lip balm is based on wild-collected African shea butter from a women’s cooperative, and lightly scented with the marvelous, unique, citrus-y essential oil of neroli.
Shea butter is a natural sun-blocker, so it really helps prevent chapping in all seasons. Kisu is still, by far, Eve’s favorite lip balm!
Lamborn Mountain Farmstead

Lamborn Mountain’s organic lavender and goat milk body-care products, made on a small organic farm in Paonia, CO, by our friends Carol and Jim Schott, are a great favorite at Harlequin’s.
From the milk of their own goats and lavender from their fields, they make the most luxuriously creamy, moisturizing hand and body lotion and gentle aromatic soaps. We offer their lavender lotion, their calming and uplifting Lavender Hydrosol, and Cleopatra’s Bath gift Sets. All Lamborn products are hand-made in small batches.
Dr. Brawner’s Healing Aftershave – Harlequin’s Exclusive!
 Formulated and made in Boulder by ‘the doctor’ himself (our founder, Mikl Brawner), from 99% pure Aloe Vera Gel, with cold-pressed, organic Rosehip Seed Oil; 100% pure Jojoba Oil, and 32,000 IU Vitamin E Oil, along with essential oils of Lavender, Vetiver, and Rose. That’s all. No alcohol, nothing synthetic, non-greasy. All the ingredients are natural plant products, chosen for their skin-healing qualities. The steam-distilled Rose Oil is a powerful anti-viral and antiseptic. The other ingredients are good for healing burns and dry and damaged skin, inflammation, wrinkles. They are moisturizing and uplifting to the spirits.
Formulated and made in Boulder by ‘the doctor’ himself (our founder, Mikl Brawner), from 99% pure Aloe Vera Gel, with cold-pressed, organic Rosehip Seed Oil; 100% pure Jojoba Oil, and 32,000 IU Vitamin E Oil, along with essential oils of Lavender, Vetiver, and Rose. That’s all. No alcohol, nothing synthetic, non-greasy. All the ingredients are natural plant products, chosen for their skin-healing qualities. The steam-distilled Rose Oil is a powerful anti-viral and antiseptic. The other ingredients are good for healing burns and dry and damaged skin, inflammation, wrinkles. They are moisturizing and uplifting to the spirits.
Mikl has made and used this formula for more than 20 years to heal his Irish skin from the abrasion of shaving and the drying effects of the Colorado sun (and keep him looking youthful and handsome!). And it smells wonderful, and it’s not just for men! Women love using it as a premium facial moisturizer, and on shaved legs.
Cold Weather and Snow Preparation and Protection
 As Colorado gardeners, we’ve come to expect snow in October (last year it was October 10), but September?! In the past 24 hours, we saw a temperature swing of more than 60 degrees, going from record-breaking heat to one of the earliest recorded snow falls in the state (the earliest recorded area snowfall was in 1961 when Denver received over 4″ of snow on Labor Day).
As Colorado gardeners, we’ve come to expect snow in October (last year it was October 10), but September?! In the past 24 hours, we saw a temperature swing of more than 60 degrees, going from record-breaking heat to one of the earliest recorded snow falls in the state (the earliest recorded area snowfall was in 1961 when Denver received over 4″ of snow on Labor Day).
This translates into a lot of flower, fruit, and vegetable crops cut short, and a lot of unanticipated work protecting vulnerable plants, harvesting, and preserving. How many of you spent Sunday and Monday making pesto, tomato sauce, pickles, jam, and flower bouquets?[Read More]
Garden Magazine’s 2019 State of the Industry Report
This fall, Garden Magazine’s Matt Mcclellan interviewed Mikl to find out more about our sustainable approach to growing plants and how it appeals to our conscientious customers. Read the article here
Seed Dreaming
By Eve Reshetnik Brawner
“Every day, millions upon millions of seeds lift their two green wings” (Janisse Ray)
(Okay, if it’s a ‘monocot’, it only lifts one green wing, but we can allow a bit of poetic license)
I love seeds. They’ve fascinated me since early childhood. Some of my earliest memories involve examining maple samaras, sycamore balls, acorns and pine cones, and planting peas and Sweet Alyssum and lima beans in cut-off milk cartons on the kitchen windowsill. I am still in awe of the power packed into a seed. [Read More]
PUTTING YOUR GARDEN TO BED
 It’s the time of year to ready our gardens for the upcoming fallow winter season and prepare for next year’s growth. We do this knowing that regeneration will be occurring in our soil, with the microbes and with overwintering insects. Here are tips for you to best help this process take place, while still having an aesthetically pleasing garden. [Read More]
It’s the time of year to ready our gardens for the upcoming fallow winter season and prepare for next year’s growth. We do this knowing that regeneration will be occurring in our soil, with the microbes and with overwintering insects. Here are tips for you to best help this process take place, while still having an aesthetically pleasing garden. [Read More]
RELAX! RECONSIDERING GARDEN CLEAN-UP

Autumn has declared itself on the Front Range, and many gardeners are itching to bring a close to the gardening year by tidying up. But wait! There are some important issues to consider here before bringing out the rakes, blowers, clippers and shears.

Now is a great time to take a long look at your gardens and make notes on successes, disappointments, gaps, and changes that you’d like to make. Assess the ecosystem you have created, and think about how you can make it even more supportive of our precious wildlife, beneficial insects, pollinators and soil life.
A certain amount of garden clean-up is very important for reducing diseases and pests that are difficult to control. If you haven’t already done so, do remove diseased plants from your vegetable garden. You should have been removing and treating diseased foliage from roses or shrubs with fungal diseases like mildew, blackspot or rust before now, but if their disease-carrying foliage is falling now, keep them picked up and dispose of them responsibly.

But don’t be so quick to scalp those perennials and annuals! Many of them provide natural food and shelter sources that wildlife and beneficial insects depend on for winter survival. You may not have noticed, but so many beneficial insects and butterfly larvae spend the winter in the (often hollow) dead stems. If you throw them out, you’ll lose most of the beneficials that would otherwise keep the balance next year. Always keep an eye out for egg cases attached to stalks when you prune or clean up. There’s often an aesthetic side-benefit – many seed-heads look fabulous either crowned with snow or silhouetted against the snow-covered ground.
Some perennials die back to below ground (peonies, false indigo, gas plant, golden banner, balloon flower, desert four o’clock, gayfeather, leadwort/plumbago, etc.) leaving no basal growth and leaving a completely blank space. To make sure you don’t forget where they are and accidentally dig them up or step on them, leave dry stems until the new growth begins to appear in spring.
 Unless you have an ‘ornamental’ grass that self-sows aggressively, leave grasses and their seedheads standing. If they are ‘cool-season’ grasses, you’ll want to leave them until about mid-February, then cut them to 3” above the ground so they can begin making unimpeded new growth as soon as the soil thaws. Dormant ‘warm-season’ grasses can remain attractive until warm weather comes and don’t need to be cut down until April.
Unless you have an ‘ornamental’ grass that self-sows aggressively, leave grasses and their seedheads standing. If they are ‘cool-season’ grasses, you’ll want to leave them until about mid-February, then cut them to 3” above the ground so they can begin making unimpeded new growth as soon as the soil thaws. Dormant ‘warm-season’ grasses can remain attractive until warm weather comes and don’t need to be cut down until April.
Leaving dry stalks standing in the winter also helps preserve soil structure. Snow collects between the stalks and provides protection from freezing temperatures by insulation for the crowns of the plants, especially important for marginally hardy plants. Captured snow keeps soil temperature more consistent, protecting from extreme temperature fluctuations, and helps prevent the alternate freezing and thawing that can disrupt mycorrhizal networks (and uproot plants, especially new and small ones).

Leave the leaves! The larvae of many butterflies overwinter in the blanket of autumn leaves, as well as other beneficials. The leaves also provide cover for frogs, toads and spiders. Songbirds eat more than just seeds; they search in the leaf litter for insect eggs and caterpillars. As leaves naturally break down over time, they feed the soil microbes that make nutrients available to plants. Worried about harboring snail and slugs? Before those leaves begin to fall, spread a non-toxic slug bait like Sluggo in areas of concern. You may want to remove leaves and twigs from patios, decks, walkways and lawns, and that’s fine – especially if you can spread them under shrubs or pile them in a corner where they’ll remain undisturbed through the winter. And very large, flat leaves from trees like Catalpa, Basswood (Tilia americana), Norway Maple, Sycamore/London Planetree) should be cleared from beds or they can form a slick solid mat that smothers the crowns of smaller plants.


Xeriscape: Native Plants
Achillea lanulosa (Achillea millefolium var. lanulosa) (Yarrow)
Agave parryi neomexicana
Amelanchier alnifolia (Serviceberry)
Amorpha canescens (Leadplant)
Aquilegia barnebyi
Aquilegia caerulea (Rocky Mt. Columbine)[Read More]
Climate Strike 2019
“On September 20th, young people and adults across the US and world will strike to tell the UN and leaders across the world that we want climate action. By growing and uniting the multi generational climate movement, the strike is the launch of a new era for just and equitable climate action.”
Harlequin’s Gardens is joining the Climate Strike, Friday Sept. 20th, by striking while the iron is hot, increasing the focus on the Climate Crisis.
 At Harlequin’s Gardens we will not be leaving our jobs on September 20. Instead we will be at work for Harlequin’s where we are always working to help you and the planet. AND we will be giving away one Free bag of compost with each purchase, on Friday, the 20th.[Read More]
At Harlequin’s Gardens we will not be leaving our jobs on September 20. Instead we will be at work for Harlequin’s where we are always working to help you and the planet. AND we will be giving away one Free bag of compost with each purchase, on Friday, the 20th.[Read More]
2019 Tomato Tasting Results
This year’s tomato tasting was a great success, with a total of 41 tomato varieties present over the 3-hour event!
Participants brought in some wonderful new varieties this year, including Pink Bumble Bee Cherry, Gajo de Melon, and Blue Cream Berries. We always take people’s votes into account when deciding which tomato varieties to carry, so look for the most popular varieties from this year and previous years when you come to buy your organic tomato starts next spring at Harlequin’s Gardens. Every year we grow 80+ great varieties for all kinds of uses and growing conditions! A huge thank-you to Growing Gardens for providing our the location, helping us publicize the event, and for bringing us some fabulous volunteers. Thank you also to the volunteers of Slow Food Boulder County. We couldn’t have done it without you!

2019 Taste of Tomato Vote Tally
Lycium (Goji Berry)
Whoever heard of Goji Berry 20 years ago? Now, with the current interest in superfoods, phytonutrients and antioxidants, Goji Berry juice and dried fruits can be found in many urban grocery stores. The 70+ species of Lycium are found on most continents and one species, Lycium pallidum, is native to Colorado. But the best known and most grown Goji is Lycium barbarum, the Chinese Wolfberry, also known as Matrimony Vine, Desert Thorn and Boxthorn. What is not commonly known is that this exotic superfood can be easily grown in Colorado.[Read More]
Insectary Plants: Let Nature Manage the Pests
It’s a common idea that Nature, left to its own devices, comes to some kind of balance. If one organism gets too numerous, something else will increase to reduce that population. In the case of monocultures created by humans, there is an enforced imbalance that has to be propped up with lots of energy and effort. So in the pursuit of sustainability, humans are opening our eyes to the possibility of biomimicry, imitating Nature. We are coming to the realization that biodiversity is far healthier and less energy intensive than monocultures born out of the aggressive hubris to control Nature. “Let Nature take her course.” But we can stack the deck in human favor first.[Read More]
Biological Farming & Gardening
A newer science that’s not tied to petroleum profits is emerging to challenge the industrial approach to agriculture and gardening. Enormously powerful, politically connected giants like Monsanto, Bayer, and Dupont will continue to make money, but after 60 years of dominance, the “Better Living Through Chemistry” model can no longer hide its fatal flaws. Mountains of evidence now point to the downside of chemical agriculture: poisoning the earth, driving global climate change, causing major health problems, killing pollinators, destroying the life of the soil. The good news is that a more long-range, wholistic view called Biological Agriculture and Gardening is starting to take its place.
This “new” method is based on an entirely different paradigm or model of plant culture. Instead of the bellicose mentality that birthed the pesticide-fungicide-herbicide and chemical fertilizer approach, the biological approach taps the same cooperative relationships that Nature herself has long employed successfully for survival and sustainability. Instead of seeing bacteria as germs, fungi as diseases, and insects and weeds as pests, the biological model sees Nature as brilliantly creative and diverse, and basically good. The scientific truth is that few insects, bacteria and fungi are harmful; most are beneficial or essential to plant development, plant health, and subsequently for human health.[Read More]
Xersicape: Non-Native Plants
Acantholimon glumaceum
Acantholimon hohenackeri
Acantholimon litwanovii
Achillea ‘Moonshine’
Achillea ageratifolia (Greek Yarrow)[Read More]
Narcissus poeticus – Double Albo Pleno Odorata
Double Poets Daffodil
Bulb. Z3. 16-18” tall. Blooms late spring. Compost-improved soil. Heirloom.
Full, ruffled, snowy-white blooms are a gorgeous, bright beacon in your spring garden. Highly fragrant, so be sure to place them near paths and patios where you can enjoy them. Blooms are most prolific in cool springs. Deer and rabbit resistant. Lovely combined with columbine, Icelandic poppies and bleeding hearts.
Non-Toxic Weed and Pest Control
 Non-toxic Herbicides
Non-toxic Herbicides
Summer is a successful time to kill weeds, either by mechanical weeding or with herbicides. But toxic herbicides, like Roundup are not solutions we recommend. Roundup in particular was once believed to be quite safe, but now is shown to be harmful to soil life including nitrogen-fixing bacteria, amphibians and is a probable human carcinogen. Roundup formulations can be up to 400 times more toxic than the active ingredient, glyphosate.
At Harlequin’s Gardens, we only sell non-toxic products, but not all non-toxic products are actually effective. Four years ago we tested five non-toxic herbicides and found only two to be really effective: 20% Vinegar and Avenger.
20% Vinegar is 20% acetic acid. It is a non-selective organic acid that quickly kills many weeds, then quickly biodegrades. Repeated use can acidify the soil which is usually a benefit in our alkaline soil. Be careful not to spray desirable plants, and be careful to protect your eyes, especially on windy days. It is most effective on small plants. Repeated applications may be necessary on perennial weeds.
Avenger is a citrus oil weed killer that we found to be equally effective as the vinegar. It is certified organic and is biodegradable. Avenger is non-selective so care must be taken to keep spray off desirable plants. It comes in a ready-to-use (RTU) formula and in a concentrate which may be mixed stronger for tougher, perennial weeds. Like vinegar, it is most effective on small plants, and is best sprayed during hot weather in direct sunlight.
In order to “control” bindweed and other weeds with extensive root systems, don’t let new growth get longer than 2″ or the weed will revive.
BLISTER BEETLE: We have been hearing reports of Blister Beetle attacking clematis. This is a light grey, long beetle that can defoliate a clematis vine in 2 or 3 days. We have found that an organic product called Veggie Pharm actually kills this beetle. It must be sprayed directly on the beetle. (Don’t try to pick up a Blister Beetle; they can raise a blister)
Tree Wrap: We recently saw a big buck with his antlers in the velvet stage. This the time of year deer cause the most damage, when bucks rub their itchy antlers on smooth, usually young tree trunk, tearing the bark. Sometimes a young tree can be girdled in one night. We carry a very good spiral plastic tree wrap that protects trees from deer, rabbits, sun scald in winter. It is superior to paper wraps because it lets air circulate so moisture does not decay the bark. It can be left on in the summer and it expands as the tree grows. Once the bark is older and tougher, it will no longer need protection.
Curl-Leaf Mt. Mahogany
Curl-leaf Mt. Mahogany (Cercocarpus ledifolius)
This tall shrub or short tree is a beautiful broadleaf evergreen that is native to Colorado and much of the west up to 9000’. It’s narrow, curled leaves are an adaptation to reduce exposure to drying sun and wind; consequently it is very drought resistant, needing no irrigation after being established.The leaves are also thick, leathery, resinous and dark green above and pale below. Flowers are mostly inconspicuous and the fruit is only 1/4” long with a 2”-3” long silky tail. In dry weather these tails twist like a cork screw and with a little wind can be carried a good distance and then they will screw the seed right into the soil.[Read More]
2018 Taste of Tomato Results
 This year’s Taste of Tomato was a blast! We love the new location at Growing Gardens’ Barn, with its’ beautiful view of the Flatirons, easy access, and wonderful staff. The tasting featured 44 different varieties of tomatoes, with Aunt Ruby’s German Green winning the greatest number of votes. Participants brought in some wonderful new varieties this year, including Brad’s Atomic Grape, Thornburn’s Terracotta, and Indigo Cherry. Look for the most popular varieties from this year and previous years when you come to buy your organic tomato starts next spring at Harlequin’s Gardens. Every year we grow 80+ great varieties for all kinds of uses and growing conditions![Read More]
This year’s Taste of Tomato was a blast! We love the new location at Growing Gardens’ Barn, with its’ beautiful view of the Flatirons, easy access, and wonderful staff. The tasting featured 44 different varieties of tomatoes, with Aunt Ruby’s German Green winning the greatest number of votes. Participants brought in some wonderful new varieties this year, including Brad’s Atomic Grape, Thornburn’s Terracotta, and Indigo Cherry. Look for the most popular varieties from this year and previous years when you come to buy your organic tomato starts next spring at Harlequin’s Gardens. Every year we grow 80+ great varieties for all kinds of uses and growing conditions![Read More]
Harvest Guidelines for Summer Crops
Here are a few harvest guidelines for summer crops:
Eggplants should be picked while they are still firm and glossy. Once their skins have become dull, they will be softer and have dark seeds, which can spoil the flavor. Eggplants don’t keep long, so use them soon after harvest.
Bell peppers and sweet frying peppers are sweetest when allowed to ripen fully to their mature color, yellow, orange, red, purple or mahogany. Bell peppers are often picked green, but their flavor will be a lot more pungent and they may be more challenging to digest.
Some of the hot peppers are traditionally enjoyed green – poblano, mulatto, jalapeno, Anaheim-type, while most of the rest are allowed to ripen to red (cherry, habanero, cayenne, lanterna, any chile dried for a ristra, etc.) orange (Bulgarian Carrot), or dark brown (Pasilla).[Read More]
A Xeriscape Harvest
For most people, harvest time brings to mind a cornucopia of veggies and fruits. For me, the end of this 2009 growing season has been a fruition of over 20 years of cultivating a xeriscape where most of the trees and shrubs have been watered 5 times a year or less. These self-imposed watering restrictions have demonstrated which plants can survive and thrive under serious water shortages. I have done this both to encourage water conservation in Colorado and to demonstrate that a dry western landscape can be beautiful.
The reason why 2009 feels like a harvest year is because many of my woody plants are now mature and because with all the rain we’ve been getting, my xeriscape has never looked better at the end of summer.[Read More]
Tulipa ‘Paul Scherer’ Triumph Midseason Tulip – NEW AGAIN!
 NEW for 2019!
NEW for 2019!
The darkest Triumph tulip, dramatic purple-black with a straight-sided shape. Earlier than ‘Queen of Night’ but a very similar color. Contrasts wonderfully with any color of tulip, whether your garden plan is classic or goth. Triumph tulips perennialize well in the garden if left uncut and fertilized after blooming. 16–18″ tall. Mid Spring blooms, Z3-7
Eve’s Favorite Fragrant Roses
These are among our favorite fragrant roses. While we grow and sell many of these, they are not always ready to be put out for sale, and quantities are always limited! Come by and view our current selection, and check our 2024 Rose list.
-

Banshee Rose
“Banshee” (found) Z 4, dbl pink 2″ early & long-blooming May-June, rich sweet damask fragrance; large shrub or climber, no die-back, very disease resistant, very tough & tolerant of low water, poor soil, shade, once established. Distinctive matte foliage, fall color- purple, orange. Common in old neighborhoods all along the Front Range.Not terribly prickly. Cut armloads for big fragrant spring bouquets!
- “Broadway Perpetual” (found, Boulder) Z 5 (4?) Large dbl strong pink quartered, deep old-rose perfume, spring & fall, sporadic in between. Good cut-flower. Seems somewhat shade-tolerant. Strong arching growth to 7’. Potential climber? Healthy foliage, moderately prickly.
-

Fairmont Proserpine, courtesy High Country Roses
“Fairmount Proserpine” (found, Denver)
- Abraham Darby (English) Z 4-5. Large, dbl, cupped, pink shading to apricot, repeats very well, strong scent, old-rose/fruity, good cut-flower. Heavy blooms are sometimes pendulous. Large, bushy shrub 5-6’ x 5-6’. Glossy disease-resistant foliage, stout canes are moderately prickly.
- Alchymist (Lg. Flowered Climber, lg.shrub) Blooms very large, warm apricot shades, very double, looks English, very fragrant, haven’t grown.
- Apothecary’s Rose (Gallica) Z 3. Very old; semidouble deep pink blooms in late spring on thin, erect prickly canes to 4’. Delicious sweet old-rose perfume. Tolerates some shade but may mildew. Perfect for herb garden.
- Baronne Prevost (Hyb. Perpetual) France, 1842. Z 5 (4?) Fat globular buds open to large 4″, flat, very double, loosely quartered deep “rose-pink” blooms with rich damask perfume, repeats well through season. Rather thorny, large arching shrub to 6’x6’ or more. Good for wrapping on pillar, pegging, self-pegging, or climbing.
- Cl. American Beauty (Lg. Fl. Climber) 1909 USA, Wichurana hyb. Z4 Large blooms are double, deep pink, paler on undersides, borne in small clusters on longish stems, strong Damask scent. In 1940’s considered the most fragrant climbing rose. Leaves dense & glossy, healthy. Vigorous growth to ~10’, tolerates some shade, neglect; profuse in June, sporadic repeat (esp. in cool summers).
- Constance Spry (English) Bounteous, very large double pink flowers in late spring on a large arching shrub easily used for draping or climbing. Bred from the Gallica ‘Belle Isis’. Fragrance includes a hit of ‘myrrh’, present in a number of David Austin’s English roses.
-

Darlow’s Enigma
Darlow’s Enigma (Cl. Hyb. Musk ?) Vigorous large shrub or climber of unknown origin with very disease-resistant, handsome glossy foliage. Small white semidouble flowers in clusters, borne throughout the season , are very sweetly scented. Very shade-tolerant. Zone 4.
- Desiree Parmentier (found Gallica) Probably incorrectly identified as Desiree, this rose is found in old neighborhoods throughout the Denver metro area. Healthy, soft apple-green foliage on a shade-tolerant, suckering shrub to 3’ in sun and taller in shade. Flowers are unique – many deep pink petals tightly packed, radiating out from conspicuous green ‘eye’, forming a dome–shaped blossom. Blooms in June. Rich Old-Rose perfume. Buds also unique, appearing to have had their tops cut off. Blooms are produced singly, not in clusters, making it ideal for cutting. Thrives on neglect once established. No die-back in the Denver-Boulder area. Prickles are numerous but very short and non-threatening.
- Fair Bianca (English) Lovely very double white blooms of old-rose style open flat and are produced in several flushes through the season on a shrub to 3’. Not very vigorous, but the fragrance is unique, including elements of licorice, lemon and myrrh.
- Felicite Parmentier (Alba Hyb.) An outstanding, classic old rose, with compact, bushy growth to 4-5’ tall. Foliage is matte, slightly greyish green, and completely healthy, even in considerable shade. Blooms are small (1 1/2″), blush pink, double and densely double, borne in small clusters, with exquisite fragrance that seems to match its appearance perfectly. No winter die-back in our area, hardy to at least Zone 4.
- Gertrude Jekyll (English) Bred from the Portland rose ‘Compte de Chambord’, which may be a better rose. Gertrude got HUGE in my garden, to 9’ tall, likes to bloom mostly at the top of the canes, hasn’t repeated very well, and is incredibly well-armed. Nevertheless, she’s worth growing for her fabulously fragrant, large, oldfashioned, double,flat pink blooms. Best grown with strict discipline (hard pruning) and protective armor.
- Golden Celebration (English)
-

Golden Wings
Golden Wings (Shrub) A healthy, vigorous, open shrub to 5-6’ tall and wide, with large, almost single lemon yellow blossoms accented by showy dark red stamens. The petals fade quickly to white in our strong sun. Blooms all season. Keep dead-headed ‘til August , then allow it to form attractive red hips. Hardy to Zone 5, maybe 4.
- Heritage (English)
- Jude the Obscure (English) Weird name for a gorgeous flower, double, globular, shading from cream to yellow to apricot, sometimes pinkish. Flowers ball in wet or very hot weather. Blooms occur in clusters of 3 to 8. Strong fruity fragrance with elements of peach, mango, etc. With disciplinary pruning, the shrub will be 5’x5’. Bright green foliage is moderately disease-resistant; Keep dead-headed to ensure good repeat.
- Konigen von Danemark (Alba) The deepest colored of the Albas, Konigen bears medium pink, very double, 2″ flowers in June, blessed with delicious Old Rose fragrance. Totally healthy, matte grey-green foliage on arching canes to about 5’. Tolerates some shade. Hardy to Zone 4.
- Louise Odier (Bourbon) Fully double, 2″ camellia-like pink blossoms are borne in great profusion in late spring, and again in pretty good numbers through the season. The fragrance is rich Old Rose. The shrub is very vigorous, theoretically to 5’x5′, but mine is 9’x9′, suggesting the need for a pillar, trellis or wall, or strong pruning. Mine never suffers any die-back, and is pretty healthy. Repeat bloom is best if you deadhead until some time in August. Pretty thorny, but not as bad as Gertrude.
- Madame Hardy (Damask) One of the most choice Old roses. Beautiful, medium-sized pure white blooms with a green button eye on a robust, upright shrub to 5’-6’ tall. Very fragrant. June blooming, Zone 4.
- Madame Isaac Pereire (Bourbon) France, 1881. Large, purplish, deep pink, cupped blooms are sumptuous in their appearance and perfume. Blooms are carried on short laterals from strong, large canes, and can be used as a climber to about 7’. Blooms are best if protected from very hot sun, but the plant is not really shade-tolerant. Hardy to Zone 5.
- Mister Lincoln (Hyb. Tea) Black-red buds open to cherry red, richly fragrant at all stages. Blooms are large (4-4.5″), double, scrolled, high-centered, good cut. “Bush is upright and almost naturally urn-shaped, to 3’ or taller. Susceptible to mildew. Robust grower, reliable bloomer.” I haven’t grown this one yet.
-

Morden Sunrise
Morden Sunrise (Canadian Shrub) A compact shrub, to about 3’x3’. Seems pretty tough in our test/display garden. Semi-double flowers open from orange buds, are 2 1/2 to 3″wide and shade from soft, tawny yellow to apricot pink, to orange. Moderately strong Tea rose fragrance is unusual for a Canadian rose, which are generally scentless. Hardy to Zone 3, almost continuous blooming.
- Nuits de Young (Moss)Laffay, France 1845. A must for its fabulously purple flowers, this rose has also been called “Old Black”. Flowers are almost double, very fragrant, with velvety maroon-purple petals emphasized by golden stamens. Mossing on buds and flower stems has a pleasant lemony pine scent when rubbed. The shrub is compact and erect, to 3 or 4’ tall, and suckers. Foliage is small and dark green. We found this rose growing in Boulder’s Columbia Cemetery, where it has survived mowing, drought, and complete neglect for at least 65 years.
- Pink Peace (Hyb. Tea) France, 1959. Enormous, intensely fragrant, very bright pink, double, with somewhat old-fashioned form, sumptuous flowers throughout the season on an upright bush. A slow starter, not exactly vigorous, but worthwhile for the blooms, which are long-lasting when cut. We know one bush in Paonia that’s about 40 years old, 4.5’.
- Reine des Violettes (Hyb. Perpetual)
-

Rosa spinosissima
Rosa spinosissima (Scotsbrier) (Species) My favorite species rose, as it perfumes my gardening hours with its strong, very sweet scent – one of the few fragrances that really carry in our dry air. The 4’ tall shrub is shade tolerant, and has very small leaves on gracefully arching canes that are covered with the lovely pure white single blooms for about 2 1/2 weeks in May. Hardy to Zone 3.
- Rosa Mundi (Gallica) Ancient, sport of Apothecary’s Rose. Named for Rosamond Clifford, mistress to Henry II. Identical in all respects to Apothecary’s, except: Dramatic semi-dbl blossoms blush-white randomly striped & splashed with crimson & pink. Petals dry beautifully for potpouri.
-

Rose de Rescht
Rose de Rescht (Portland or Damask Perpetual) A very distictive Old Rose, supposedly discovered in Iran. The flowers are small, 1 1/2″ or slightly larger, rich fuschia-red with strong purple tints, aging to magenta, very double, tightly formed rosettes, almost pom-poms, produced in small clusters amid lots of foliage. Exceptional strong Damask fragrance. Excellent repeat. The shrub is healthy, compact and bushy, to 4-5’ tall and wide. Canes are quite prickly. Hardy to Zone 4.
- Rose du Roi (Portland or Hyb.Perpetual) Lelieur, France 1815. This is a rose with a story. Bred by a French nobleman loyal to Napoleon (the second one), it was appropriated and re-named by the King, Henri XV, when he regained power. It’s also an important rose for having introduced “red” color to rose breeding in 19th century Europe. The plant is compact and bushy, growing 3-4’ tall and wide, with large leaves (I’ve noticed they’re light green in spring, with later growth being dark green with grey undersides), and prickly canes. The flowers are fabulous, fairly large, double, red mottled purple with pink reverse, loosely formed when open, and very richly scented. Repeats, with especially good display in early fall. Hardy to Zone 4-5.
-

Sharifa Asma
Sharifa Asma (English) Slow to establish, but worth the wait. Blooms are large, double, delicate shell pink, cupped, and blessed with a strong Old-rose and fruity (litchi) fragrance. Leaves are dark green, slightly leathery, and healthy as long as the shrub is not in too much shade. Growth is upright to 4’.
- Stanwell Perpetual (Hyb. Spinosissima) The earliest repeat-blooming rose to begin flowering in my garden, vying for 1st with Reine des Violettes. Bred from R. spinosissima and Autumn Damask. Canes are very prickly, arching, dark red, clothed in very fine-textured foliage, and loaded with blooms in several flushes through the season. Flowers are double, small to medium-sized, blush pink opening flat and fading to white. Very sweetly scented, with characteristics of both parents. Growth is awkward the first few years, but then fills out nicely. Hardy to Zone 4.
- Sweet Chariot (Mini) Tall for a miniature, to 2’. Small foliage and small pom-pom flowers in large clusters, unusual purple-pink color and lovely fragrance. Blooms repeatedly through season. Hardy to Zone 5.
- Sydonie (Hyb. Perpetual) Extremely reliable repeat bloom, exquisite Damask fragrance, unique flower form. Flowers are “rose-pink”, 2-2 1/2″ very double, very quartered, with strongly in-curved center petals. They are borne on very prickly arching canes on a bush that’s supposed to be 3 1/2’ tall and wide. NOT. Mine is 8’x8’ and I’m planning to do some hard pruning. Hardy to Zone 4-5, I’ve never had any winter die-back.
- Tradescant (English) I haven’t grown this one yet, but I’ve seen it elsewhere and loved the blooms. They are velvety black-red, very double, opening flat and quartered, 2-2 1/2″ wide, with a powerful Old Rose fragrance. Good cut-flower, holding its shape and color several days. Hardy to Zone 5. Reportedly grows best with hot summer weather.
- Wise Portia (English) Compact, to 2 1/2’, I grow 2 of these planted very close together to form one shrub. Very large double flowers are a unique raspberry red, rosette shaped, with uniquely pointed, lotus-like petals. Heavy-blooming, richly scented, borne singly or in sprays. Excellent repeat if kept dead-headed ‘til late summer. Then it will form large, red hips. Modern-looking medium green foliage. Provide good light and good air circulation.
- Zephirine Drouhin (Climbing Bourbon) Bizot, France 1868. Hardy to Zone 5-6. Our strain is definitely hardy in Boulder/Denver. Completely thornless, somewhat shade-tolerant, vigorous tall shrub or climber to 12’ on wall or arbor. New foliage and canes are burgundy colored. Flowers are loosely double, warm deep pink, medium-sized, profuse in spring and repeats regularly into autumn. Strongly scented- fruity Old-Rose.
Some fragrant roses to try at higher elevations:
Alba Semi-plena
Alba Suaveolens
Maiden’s Blush
Chloris
Konigen von Danemark
Rosa spinosissima
Rosa rugosa alba
Rosa rugosa ‘Magnifica’
Metis
Banshee
Gallica roses
Centifolia roses
Therese Bugnet
Morden Sunrise
Rugosa roses
A Soil Revolution
In this article, Mikl explains why Soil Health matters.
From Peak Soil to Soil Revolution
 We are having a real revolution in our relationship with our soils. The turning point is our change in focus from soil fertility to soil health. In the last 60 years of the “Green Revolution” (i.e. the petrochemical boom), soil was viewed as a physical structure and fertility was viewed as a measure of chemicals in the soil — primarily NPK, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. The petroleum industry could make these macronutrients from natural gas, which make plants grow but often in poor health. Weak plants attract insect pests and fungal diseases, so more petroleum in the forms of insecticides and fungicides added to the success of the oil industry. But this approach has led to “Peak Soil” where land is losing productivity, crops are losing nutritional value, the soil is eroding at extreme rates, and the health of animals and people has declined.[Read More]
We are having a real revolution in our relationship with our soils. The turning point is our change in focus from soil fertility to soil health. In the last 60 years of the “Green Revolution” (i.e. the petrochemical boom), soil was viewed as a physical structure and fertility was viewed as a measure of chemicals in the soil — primarily NPK, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. The petroleum industry could make these macronutrients from natural gas, which make plants grow but often in poor health. Weak plants attract insect pests and fungal diseases, so more petroleum in the forms of insecticides and fungicides added to the success of the oil industry. But this approach has led to “Peak Soil” where land is losing productivity, crops are losing nutritional value, the soil is eroding at extreme rates, and the health of animals and people has declined.[Read More]
How Do We Manage Fireblight
Colorado is said to be the worst state in the US for fireblight, and 2018 was considered by many to be one of the worst years in Colorado. Fireblight is a serious disease affecting apples, crabapples, pears, Mountain Ash and hawthorn, and sometimes quince and pyracantha (supposedly up to 73 species of plants).[Read More]
Drought Resiliency
Drought resiliency is normally thought of as the ability to spring back after a drought or maybe it means tolerant of drought. But when a plant is stressed by having little water, its ability to survive and even thrive is influenced by other factors, some of which are Health, Vitality, Strength and Immune function.
The word Sustainability has become popular as a goal, but the word is too static. A more active word is Re-generative. We can “create” gardens that not only can maintain, but also support the abilities of Life to regrow, multiply, defend itself against predators and add to the vitality of other living things around it.[Read More]
July Color in the Xeriscape Garden
Xeriscape? Are you kidding? With all the rain we’ve been getting, isn’t the drought over?
As I understand our current water situation, water restrictions are still in effect for the Denver area, Colorado Springs has had a very dry spring until July and is under water restrictions, the Western Slope has been dry, New Mexico has been dry until July; and Montana and South Dakota are having severe droughts. What this means is that the wonderful moist season we are enjoying in the Denver area depends on ephemeral conditions we cannot count on. In addition, much of our water comes from the Western Slope where weather patterns can be quite different from our own, so even if our gardens are getting watered, it doesn’t mean our reservoirs will be full. We live in a semi-arid environment and water conservation and xeriscaping will be increasingly important as our population grows, especially if global warming increases our temperatures.[Read More]
On The Dry Side
Plants that can survive and even thrive with little water are always valuable in Colorado where we get 15”-18” of precipitation most years. But when a real drought comes or when limited snowfall in the mountains means water restrictions down here, then xeriscape plants are essential in our gardens
Because the well at Harlequin’s Gardens nursery is so poor, my rockery garden has been on water restrictions for the last 25 years. Here are some plants that have performed well in my garden that is watered only 3 to 7 times a year.[Read More]
Some Drought-Tolerant Gems
Plants that tolerate or even revel in hot, dry conditions are always in vogue in Colorado. We may be blessed with moisture in the spring, as we had this year, but by June or July our vegetables need regular watering and east coast woodland plants are melting. There are some plants, however that are adapted to hot and dry conditions. Some are natives and some are from other regions of the world that have similar drought stresses as we have here.
These gems are ones that we have tested at Harlequin’s Gardens where none of our demonstration gardens are watered more than once a week, and others only 5 or 6 times a year. We can recommend these plants as successful and enjoyable under mandated or self-imposed watering restrictions.[Read More]
The 2002 Drought
Drought, Water Restrictions and Gardening: How Can They Go Together?
I think we were all caught off guard by this drought, by how fast we were forced to see dying trees and brown lawns and by the difficult discipline of watering restrictions. This was especially true in Boulder and Lafayette where mandatory restrictions began in May. Actually, 2002 is the third year in a genuine drought, which some of us without city water supplies can confirm. This year all around Boulder, Red Twig Dogwoods turned brown, linden leaves were scorched, Norway Maples suffered, many viburnums were looking very stressed, and trees in medians defoliated or died. Gardeners caught in the crunch between weeks of hot, dry weather and few opportunities to water, held off most of their planting projects; some started talking about moving away to where they could garden. For Denver and other Colorado cities, next year could be much worse.[Read More]
Three Xeric Plant Select Favorites
Here are three hardy, xeric and floriferous plants that are successful in western gardens.
Russian Hawthorn, Crataegus ambiguus was tested at the Cheyenne Horticultural Station and found to be well-adapted to the west. It is native to Armenia, Iran, Russia, Ukraine and Turkey. I have a 20 year-old specimen growing without irrigation along with many native shrubs. The mature size is 15′-20′ high and wide in our area. The branches grow quite horizontally which gives it natural character. It lends itself to a bonsai/character style, and I have been growing one in a big ceramic pot for 10 years. The finely cut leaves give a soft appearance and in May it blooms with profuse white flowers that are attractive to bees and butterflies and followed by showy red berries in August/September that are eaten by birds. Very dry conditions can result in fewer flowers and fruit. Like apples, to which Hawthorns are related, the seeds contain some cyanide, so should not be eaten, but the berries are edible and make a respected heart tonic.[Read More]
Beyond GMOs and Petroleum Farming
Four years ago I was among the group of Boulder County residents who were asking to ban GMOs on our publically-owned farm lands. The Commissioners at that time voted to add GMO Sugar Beets to the already approved GMO corn, but they also increased the acreage of land to be used for organic agriculture and agreed to take another look at neonicotinoid use if there was new evidence. There is now new evidence on GMOs, Roundup that is used on 80% of GMOs and on neonicotinoids linked to the death and weakening of all our insects, including bees.
So in 2011, in order to find out if there were practical non-toxic options to manage larger pieces of farm land (like 200-300 acres), I traveled to Ohio to an Acres USA Conference. Attending that conference were over a thousand farmers and ranchers. ACRES has been guiding eco-agriculture for 45 years now; the last conference I had attended was in 1977. I met farmers and attended talks by farmers who were managing 100-1000 acres without GMOs and without toxic chemicals.[Read More]
Xeric Perennials that Thrived During the 2002 Drought
Xeriscape Perennials Thriving in 2002 Drought
Acantholimon glumacium
Acantholimon hohenackeri
Acantholimon litwanovii
Achillea ‘Moonshine’
Achillea ageratifolia (Greek Yarrow)[Read More]
Quaking Aspens
Leave them to the Mountains OR Plant them at Home?
Populus tremuloides or Quaking Aspen is not only one of the best-known native trees here in Colorado, but it is said to be the most widely distributed tree of North America. Its narrow, roughly pyramidal form is commonly 25’-30’ tall and 15’-20’ wide, although it can get much larger. The leaves are shiny, dark green above and light gray-green beneath which makes the tree shimmer in the breezes. Also its whitish trunk adds to its attractive architecture. Then in the fall the leaves can turn a rich golden yellow which look glorious on the tree and lovely on the ground. It has a suckering habit which inclines it to clumps and which has put aspen in the running for the world’s largest being.[Read More]
Bigtooth Maple
Bigtooth Maple, Acer grandidentatum, is native to the far southwest corner of Colorado in a place known as Sleeping Ute Mountain. It is common in canyons, northfacing slopes and along mountain streams in Utah, Wyoming and west Texas from 5000′ to 8000′. Although most often listed as a separate species, Bigtooth Maple is sometimes called Western Sugar Maple, therefore, a subspecies of Acer saccharum. Its other names are Canyon Maple and Wasatch Maple.[Read More]
Bur Oak
BUR OAK—QUERCUS MACROCARPA-MOSSY CUP OAK
One of the most successful oaks for Colorado is the Bur Oak. It is adaptable to our clay soils and tolerates our alkaline conditions better than most oaks. In harsh, droughty areas this tree can be a low shrub, but on rich, river-bottom land can get 170’ high and 6’-7’ in diameter; but most often grows 50’-70’ high. The trunk is often thick and short with deeply furrowed bark, and the stout branches often extend almost straight out making the tree as broad as tall. The leaves are deeply lobed only in the bottom half and these lobes are rounded not pointed as with many other oaks. The acorns are distinctive in that there is a mossy fringe around the cap. The overall effect can be quite grand and sculptural, sometimes like a Chinese painting. The short taproot is surrounded by a massive root system which is strongly competitive. This is why old specimens often are standing alone.[Read More]
Catalpa
Western (Northern) Catalpa- Catalpa speciosa
It is surprising that a tree that looks so different from the other Colorado-adapted trees, is so successful. What stands out immediately are the huge leaves which can be 3”x 6” or even 6” x “12” and are heart-shaped. And in June, this large shade tree blooms exquisite, ruffled, bell-like, white, fragrant flowers with yellow and purplish coloration .And in the fall the passerby might be surprised to see the long thin pods 10”- 18” long.[Read More]




